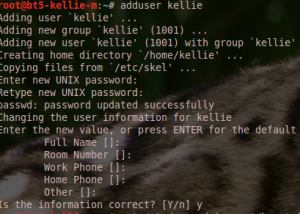
nmap is a great tool to use to perform a network ping sweep, however there is an effective way to perform a ping sweep with out any additional installation. A FOR loop can be used to perform consecutive pings.
Ping Sweep FOR Loop: FOR /L %i in (<Host Number Start (0-255)>,1,<Ending Host Number (0-255)>) do @ping -n 1 <Network Prefix>.%i | find “Reply”
The FOR loop is basically saying start at a network prefix with stated starting host number value and send a ping. Once a reply as been received the first loop is finished and it continues to the next loop. After each loop, the host number increases and a ping is sent to that address on the network. For example, say the network prefix is 192.168.0 and we want to ping host numbers (3-43). We would enter 3 as our beginning host number and 43 as are finishing host number. The one in between the two parameters states to increase each address by one for each running of the for loop. This allows us to ping each host on the the specified network range, thus performing a ping sweep.
Windows Example:
The following command ping sweeps addresses in range 192.168.100.0 – 192.168.100.255
FOR /L %i in (1,1,255) do @ping -n 1 192.168.100.%i | find "Reply"
The same function can be done in the Linux Terminal.
Linux Ping Sweep:
Linux is slightly different but follows almost the same pattern.
for i in {0..255}; do ping -c 1 -t 1 <IP PREFIX>.$i | grep 'from'; done